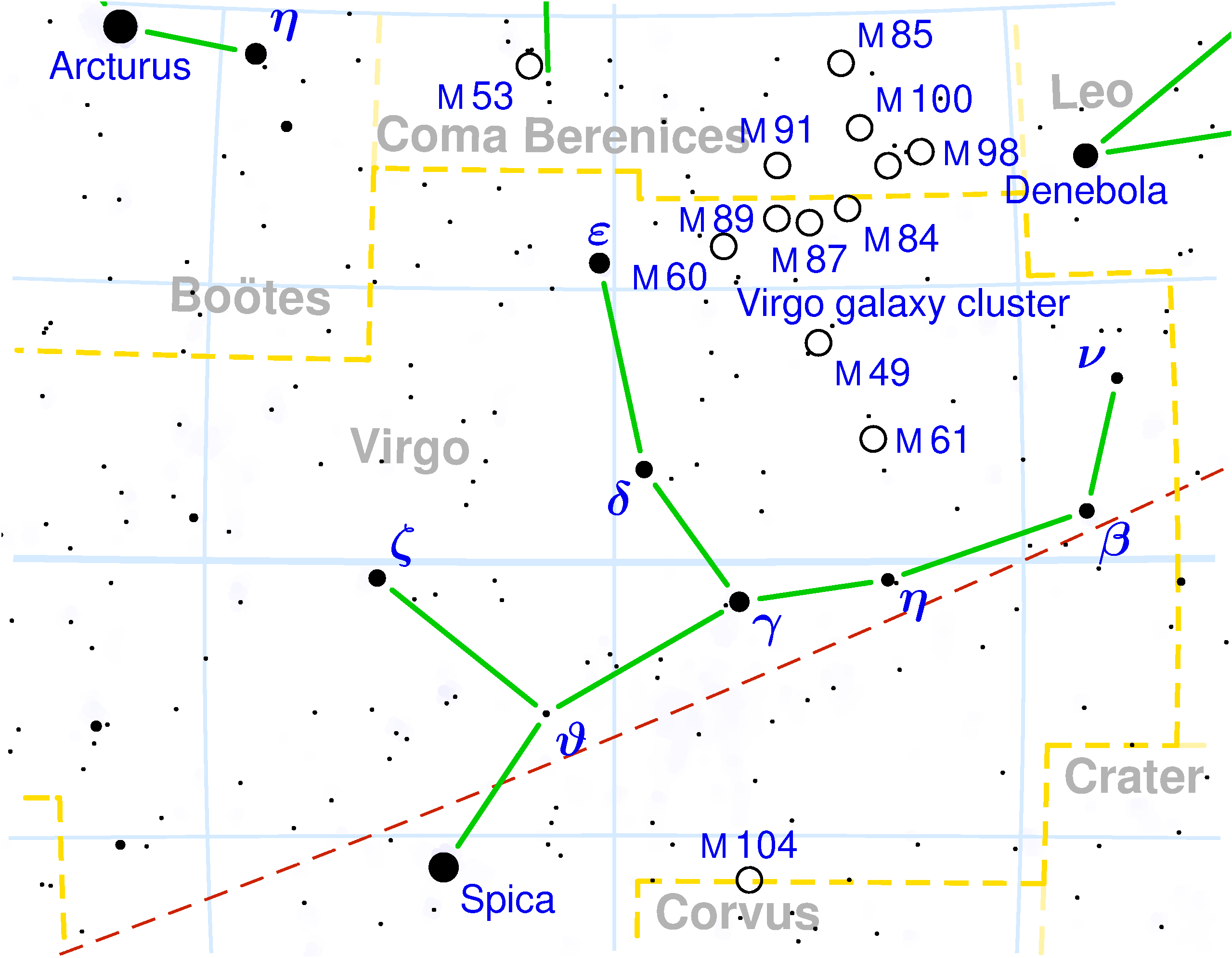
VIRGO

Till Credner - Own work, AlltheSky.com,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
Di Gerard Mercator (1512-1594) - The Mercator Globes at Harvard Map Collection [1],
Public domain, wikimedia
In Greek mythology Virgo has been identified as the virgin goddess Astraea, a daughter of Zeus, or Persephone who married Hades, or even Erigone, daughter of Dionysus, who committed suicide at the death of her father and became a constellation in the Spring sky.
Porrima is the Gamma star and is the second brightest star in the constellation. It is also a phisical double star where the two stars rotate around their center of mass in a period of 170 years. The stars are 6 billion kilometers apart, more or less the distance from the Sun to the dwarf planet Pluto. Porrima is 38 light-years from the Solar System.
The constellation Virgo is famous for its many galaxies about 40 of which can be seen with small telescopes. Among the most interesting are:

NASA/ESA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) - spacetelescope.org hubblesite.org
Public domain, wikimedia
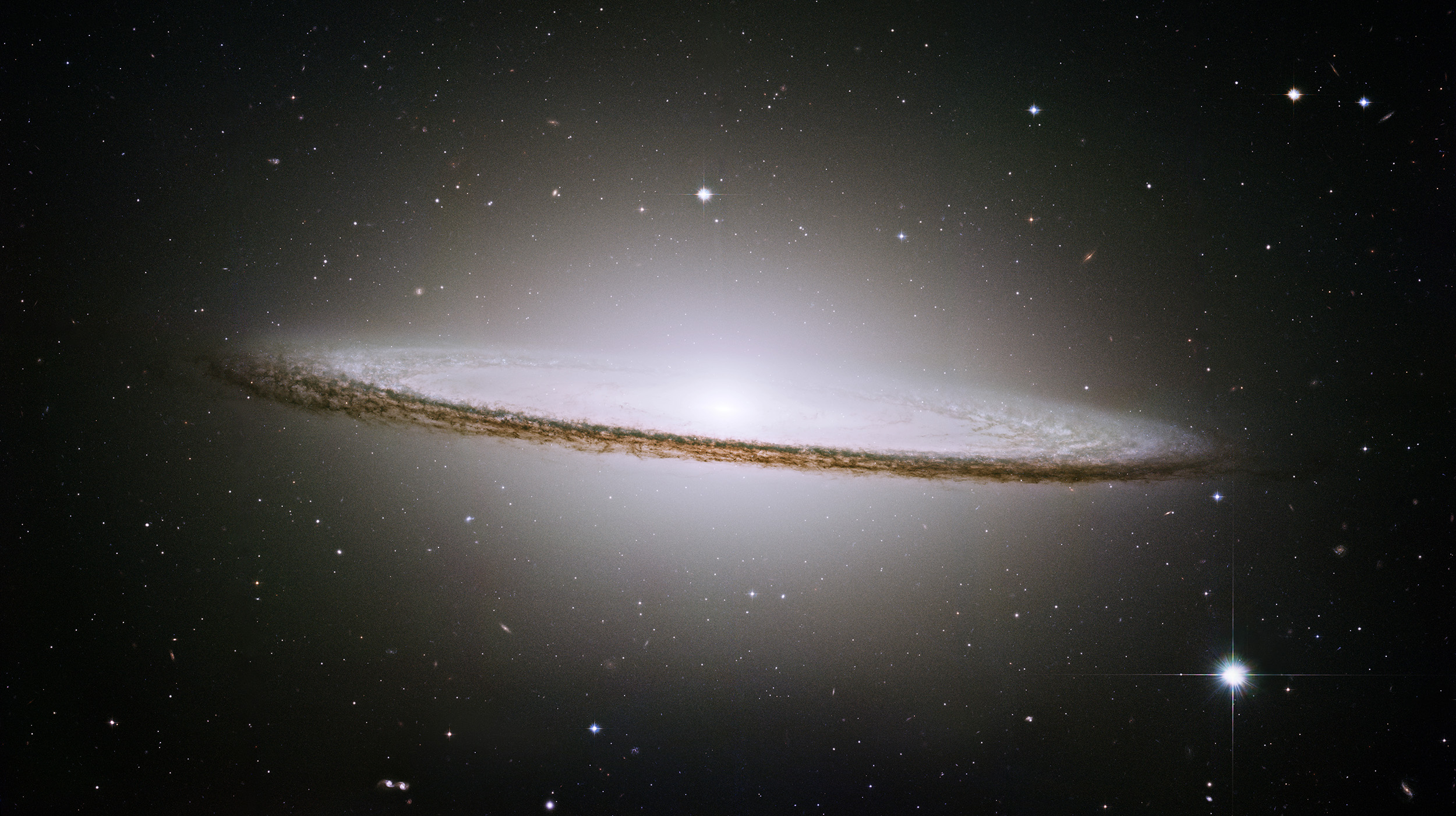
the Sombrero galaxy, M104, which takes its name from its resemblance to the typical Mexican hat. Its characteristic feature is a dense band of dust which divides it in two along its galactic equator. It is a little less than 30 million light-years away.

NASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) - HubbleSite: gallery, release. Public domain, wikimedia
M87 is a ‘monster’ galaxy with a mass equal to one trillion solar masses and a diameter 20% bigger than the Milky Way. It is thought to contain a super black hole with a mass equal to over 6 billion times that of the Sun. it is also called Galaxy Virgo A given that it is a potent radio source.
Southern Hemisphere: the constellation can be seen at the same time of the year as in the Northern hemisphere. At the southern middle latitudes, around April right after sunset it can be found more or less at the zenith.