SAGITTARIUS

Roberto Mura - Own work,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
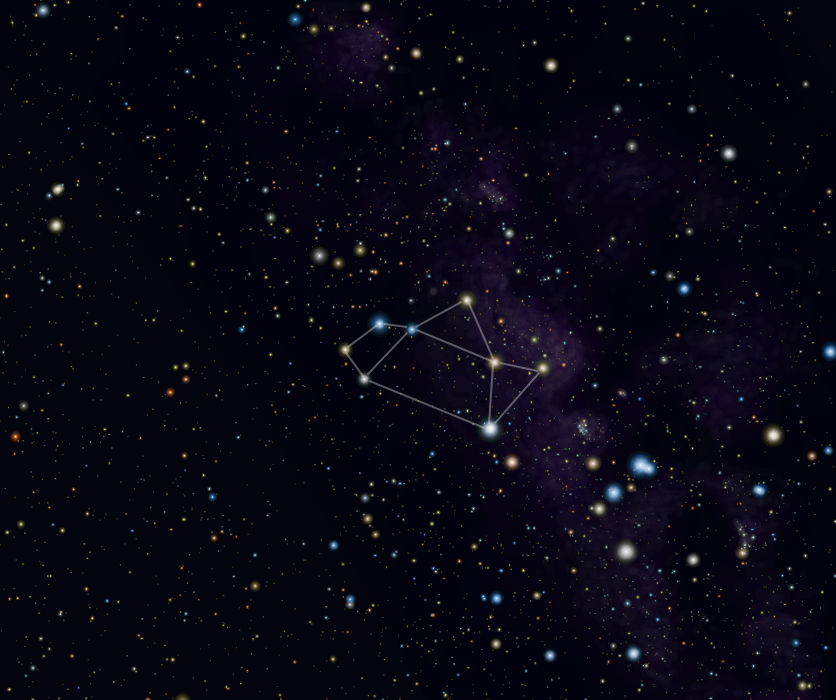
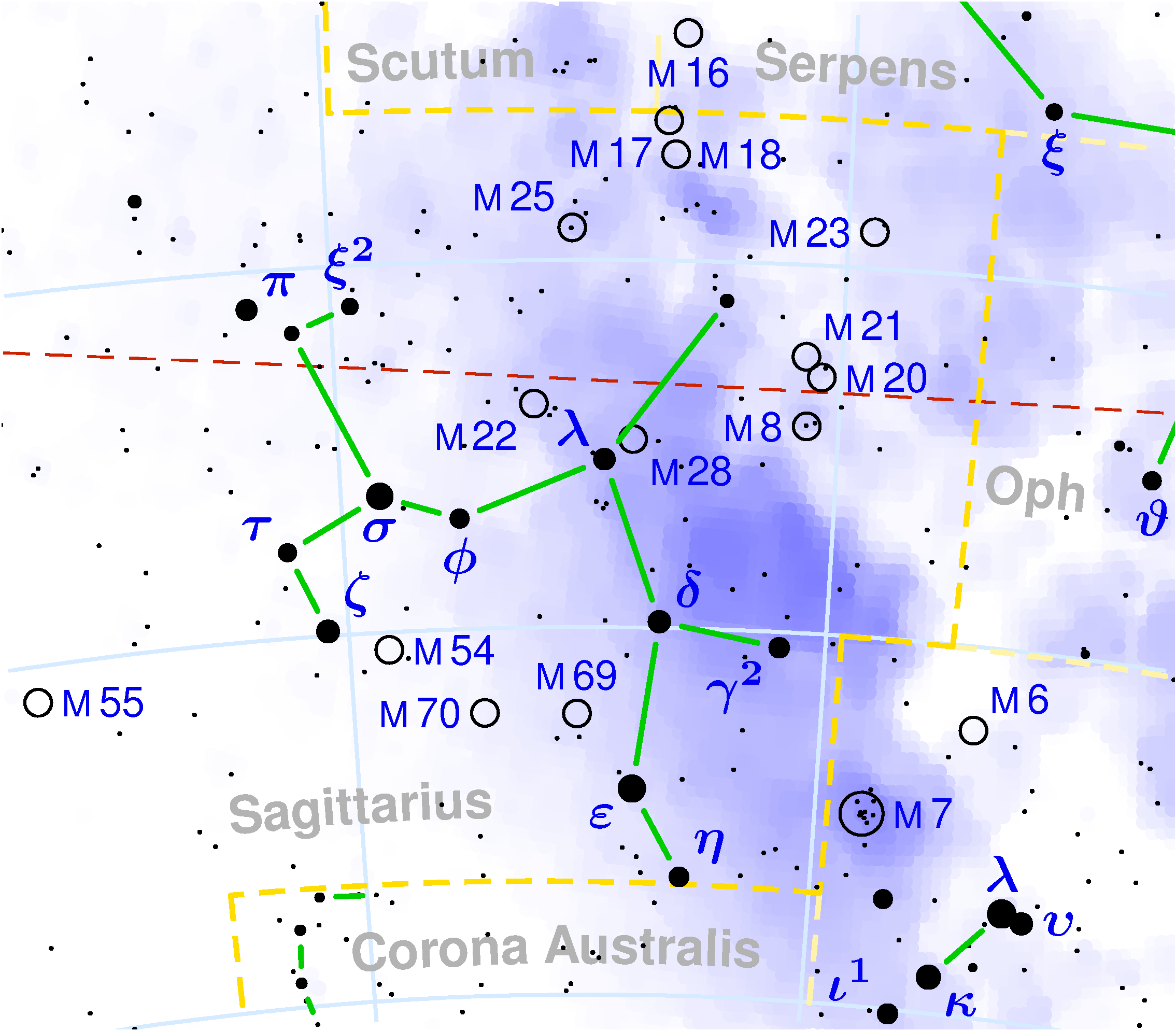
The constellation Sagittarius is one of the most prominent features of a summer sky. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of the constellation and in the southern hemisphere Sagittarius passes directly overhead. The constellation is made up of fairly faint stars but is easily recognizable either by the appearance of an archer drawing his bow or by the Teapot asterism made up of the brightest star. The Milky Way is at its densest near Sagittarius as this is where the galactic center lies. As a result, Sagittarius contains many star clusters and nebulas which make it one of the most interesting constellations in the Zodiac visible through a telescope.
Jacopo Montano - Uranographia, Johann Bode,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
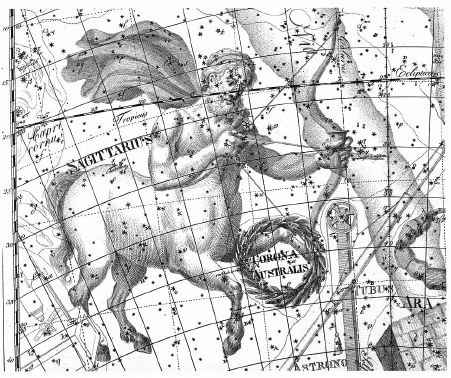
Sagittarius is commonly represented as a archer, half-man and half-horse. Although he looks like a centaur, some ancient authors described him as a satyr.
The classical nomenclature of the stars in the constellation do not correspond to their brightness. The first 3 stars are, in fact, named epsilon, sigma and Zeta.
Kaus Australis is the Alpha star. It is 143 light-years away and is a blue-white giant with an apparent visual magnitude of +1.80. It is a young star thought to be 230 million years old and is the southernmost star in the asterism of the bow.Nunki is the second brightest star but is in fact classified as a sigma star, designating the sixth position of importance. It is the brightest star in the "teapot handle". It is also a blue giant, a young star, which is 228 light-years away and is thought to be 3,300 times brighter than the Sun.
Axilla, the Zeta star, is just south of the star Nunki and is 89 light-years away. It is a white star about 30 times brighter than the Sun.
The constellation is rich in deep sky objects, among which are the three nebulas: Lagoon, Trifid and Omega and the bright globular cluster M22.
.jpg)
ESO/S. Guisard - ESO (direct link),
CC BY 4.0, wikimedia
M8 is the Lagoon Nebula. It is a bright nebula which contains an open cluster. Its name comes from a dark area of the nebula, high in dust particles, which is like a typical canal in a lagoon. It is 4,100 light-years from us and stretches over 110 light-years in length. It can been seen through a telescope.

Hewholooks - Own work,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
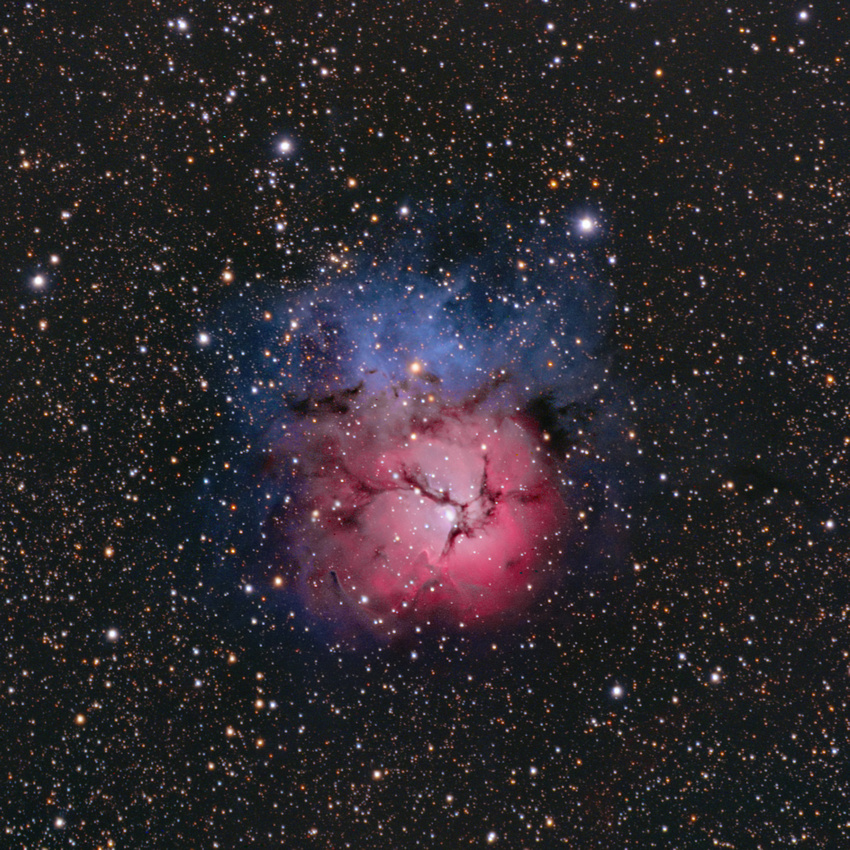
M20 is the Trifid Nebula located a little north of the Lagoon Nebula and is call Trifid due to a dark nebula at its center which divides it into three distinct parts. It can be seen through a small telescope and is located 5,200 light-years away.

Di 2MASS project - This image is from the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) project. At calltech.edu it says: "The images and image mosaics in the various Galleries are released into the public domain. 2MASS kindly requests acknowledgement in one of the following forms, the longer of which is preferred."" Atlas Image [or Atlas Image mosaic] obtained as part of the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS), a joint project of the University of Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center/California Institute of Technology, funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the National Science Foundation. Atlas Image [or Atlas Image mosaic] courtesy of 2MASS/UMass/IPAC-Caltech/NASA/NSF.,
Public domain, wikimedia
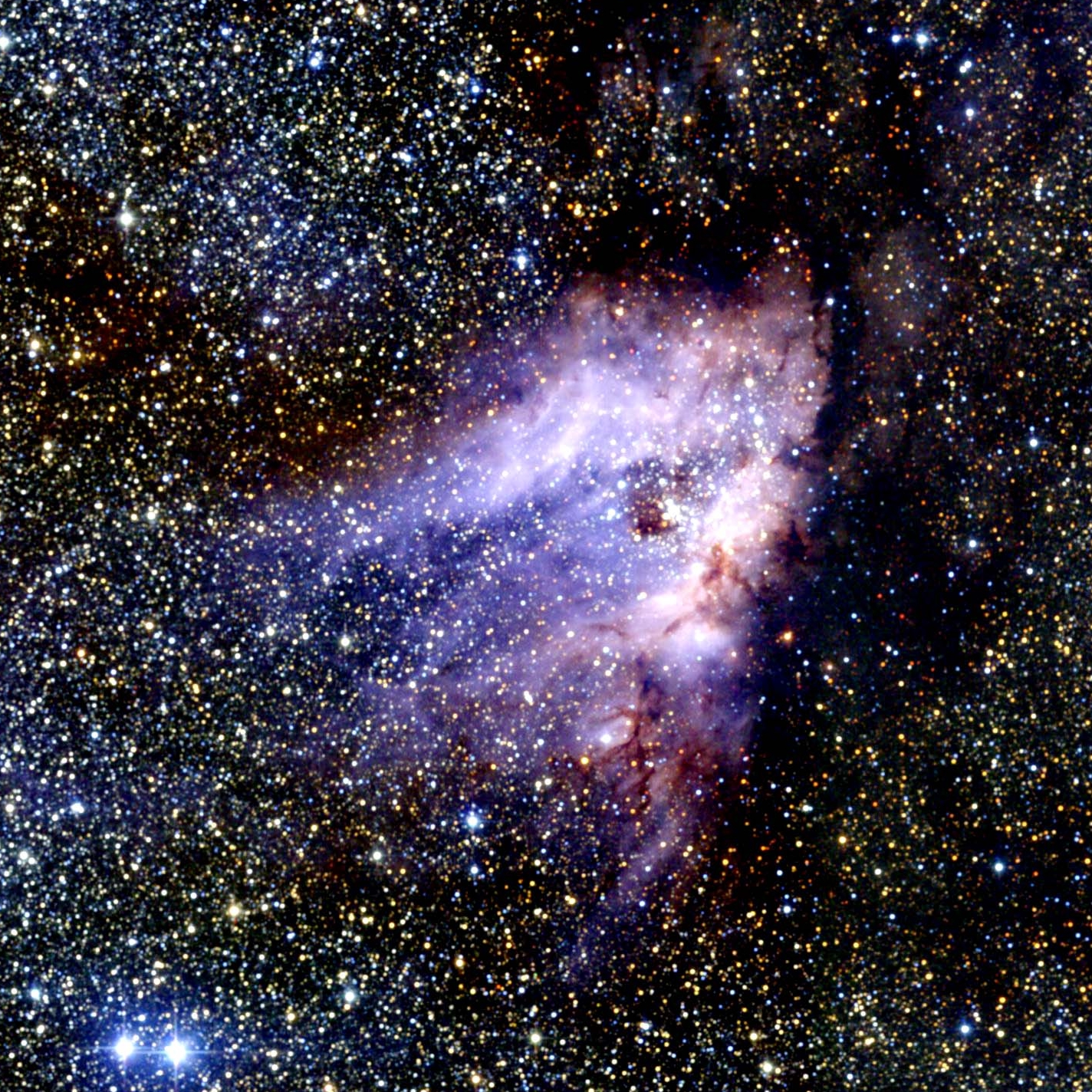
M17 is the Omega Nebula named for its shape resembling the last letter of the Greek alphabet. It is also called the Swan Nebula because it looks like a swan floating in a pond of stars when seen through a telescope. It is 6,000 light-years from us and has a diameter of 15 light-years.
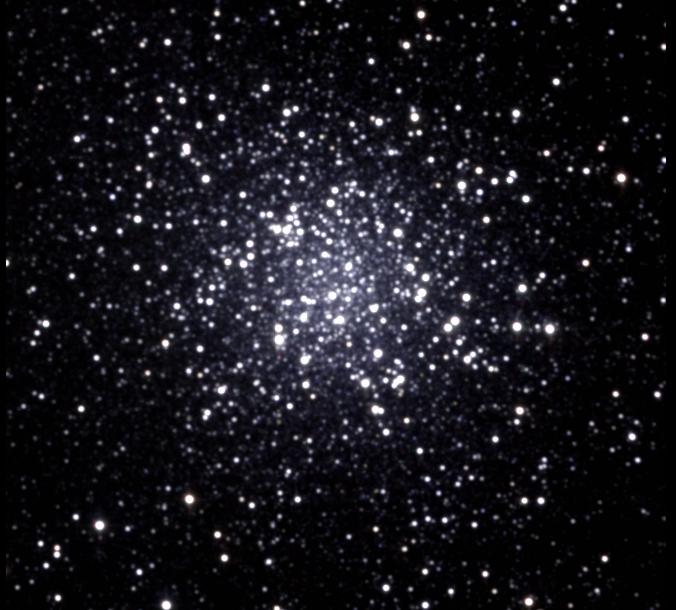

M22 is the brightest globular cluster in the constellation of Sagittarius. It is also one of the closest to Earth at 10,400 light-years away. It is visible, in theory, with the naked eye and looks like a fuzzy star.
Southern Hemisphere: Sagittarius is prominent in the southern hemisphere from May to until the end of November. At the southern middle latitudes, at the beginning of September, right after sunset, it is high on the southern horizon almost at the zenith.