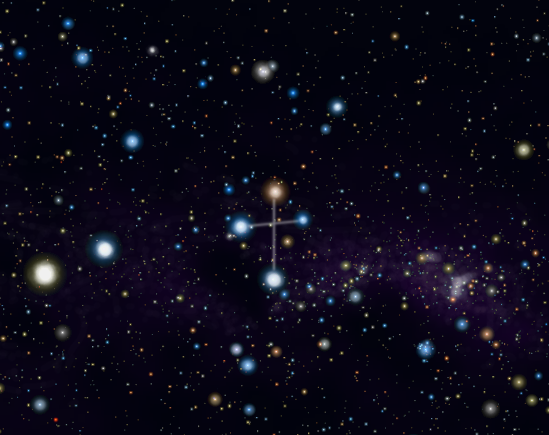
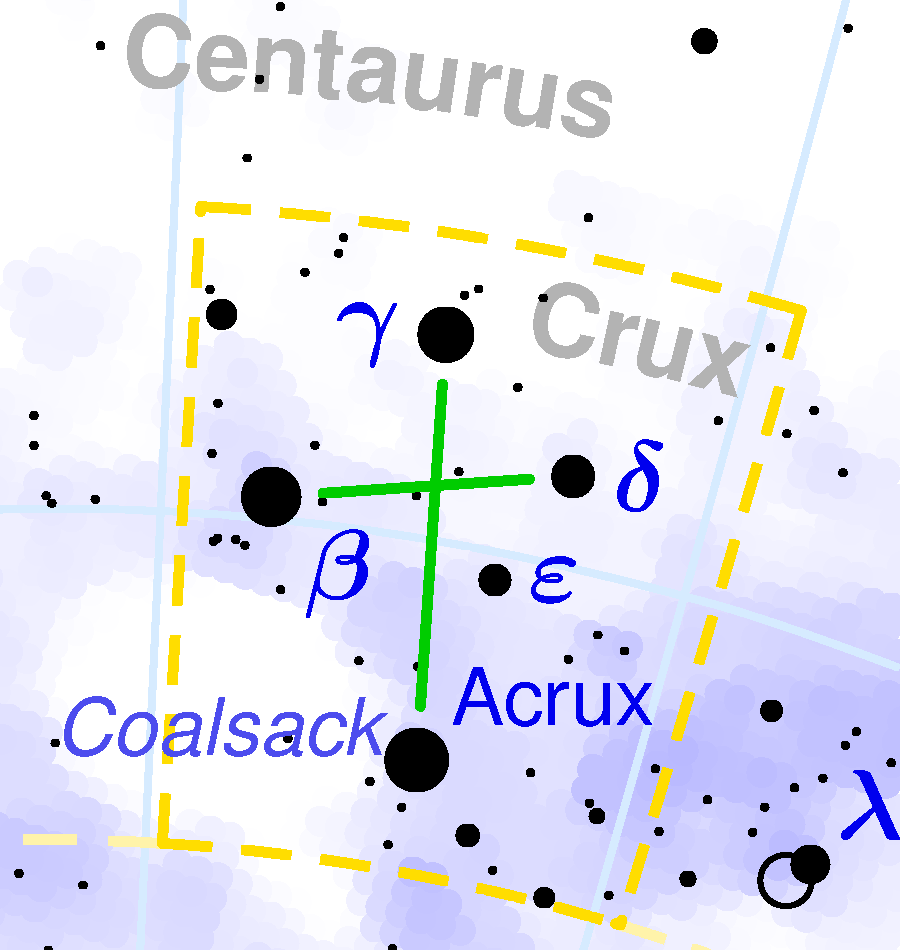
CRUX (The Southern Cross)

Roberto Mura - Own work,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
The Crux is the iconic constellation for all travelers in the Northern Hemisphere who in their eagerness to see the constellation have to push themselves to the southern latitudes or near the equator. It is the smallest constellation that we know of, a small group of stars, but with a lot of charm. If we follow the main axis of the cross from its base and lengthen it about 5 times, we can find the celestial south pole.
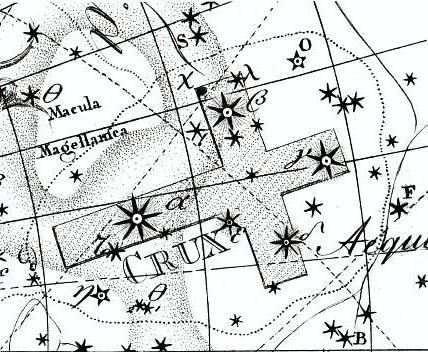
Jacopo Montano - Uranographia, Johann Bode,90
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
The Ancient Greeks and Romans easily identified the stars of the Crux because the Earth’s axis was tilted in a more favorable way for observing the sky towards the southern horizon at that time. Due to the precession of the Earth’s axis it will be visible in Italy again around 13000 AD.
The Beta star Mimosa is the left limb of the cross. It is 290 light-years from us.
The Gamma star Gacrux is the point of the cross. It is red-hued and is closer to us than the other stars at less than 90 light-years from Earth.

originally Naskies at en.wikipedia under GFDL or CC BY-SA 3.0, through Wikimedia Commons,
work derived from Coalsack_and_Dark_Doodad_Dark_Nebulae.jpg,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
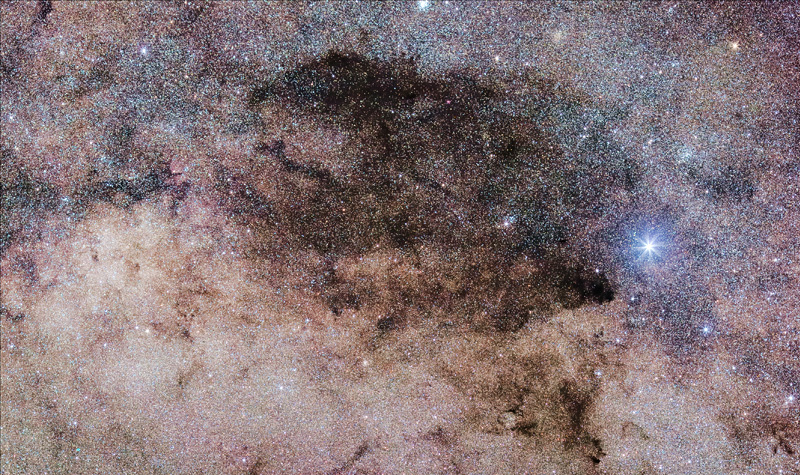
To the east of Acrux and under Mimosa we can find the dark nebula known as the ‘Coal sack nebula’ which is easily seen with the naked eye. It looks like a ‘hole’ in the Milky Way. It is an area of dust which keeps us from seeing the stars deep in our Galaxy. It is a little more than 600 light-years from us.

ESO - ESO, CC BY 4.0, wikimedia
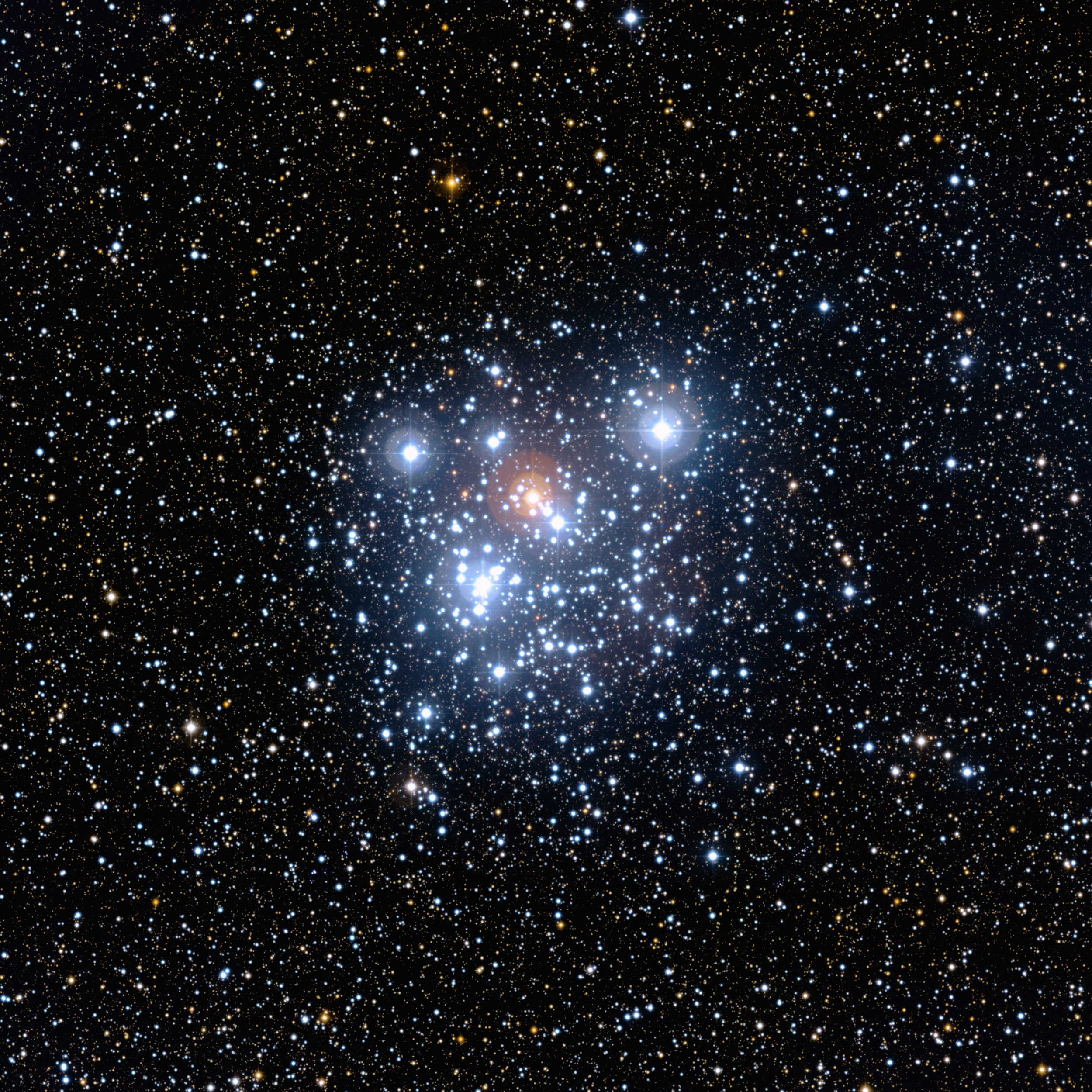
NGC 4755, known as the ‘Jewel Box’ is an open cluster which is visible to the naked eye, but with a pair of binoculars or a small telescope you can make out the 300 multi-colored stars which comprise it. It is one of the youngest clusters that we know of. It is 14 million years old and 6,400 light-years from the Earth.
Southern Hemisphere: it can be seen all year round. At the southern middle latitudes, from the end of May to the beginning of June right after sunset we find it high above the southern horizon.