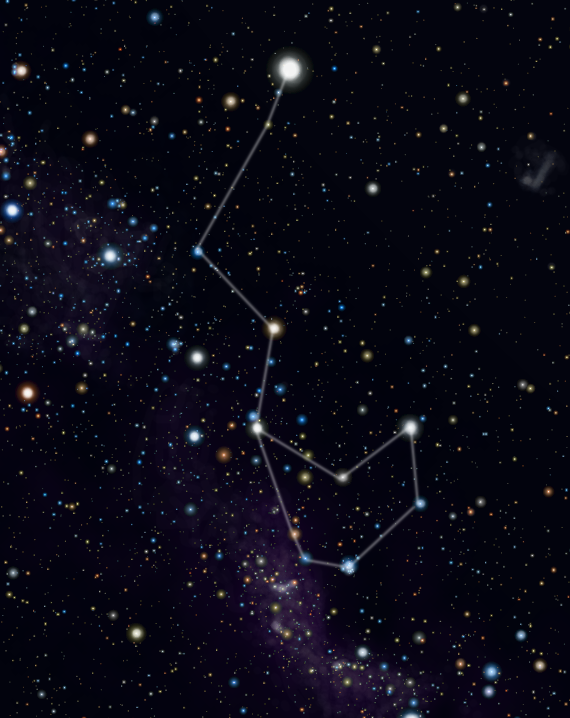
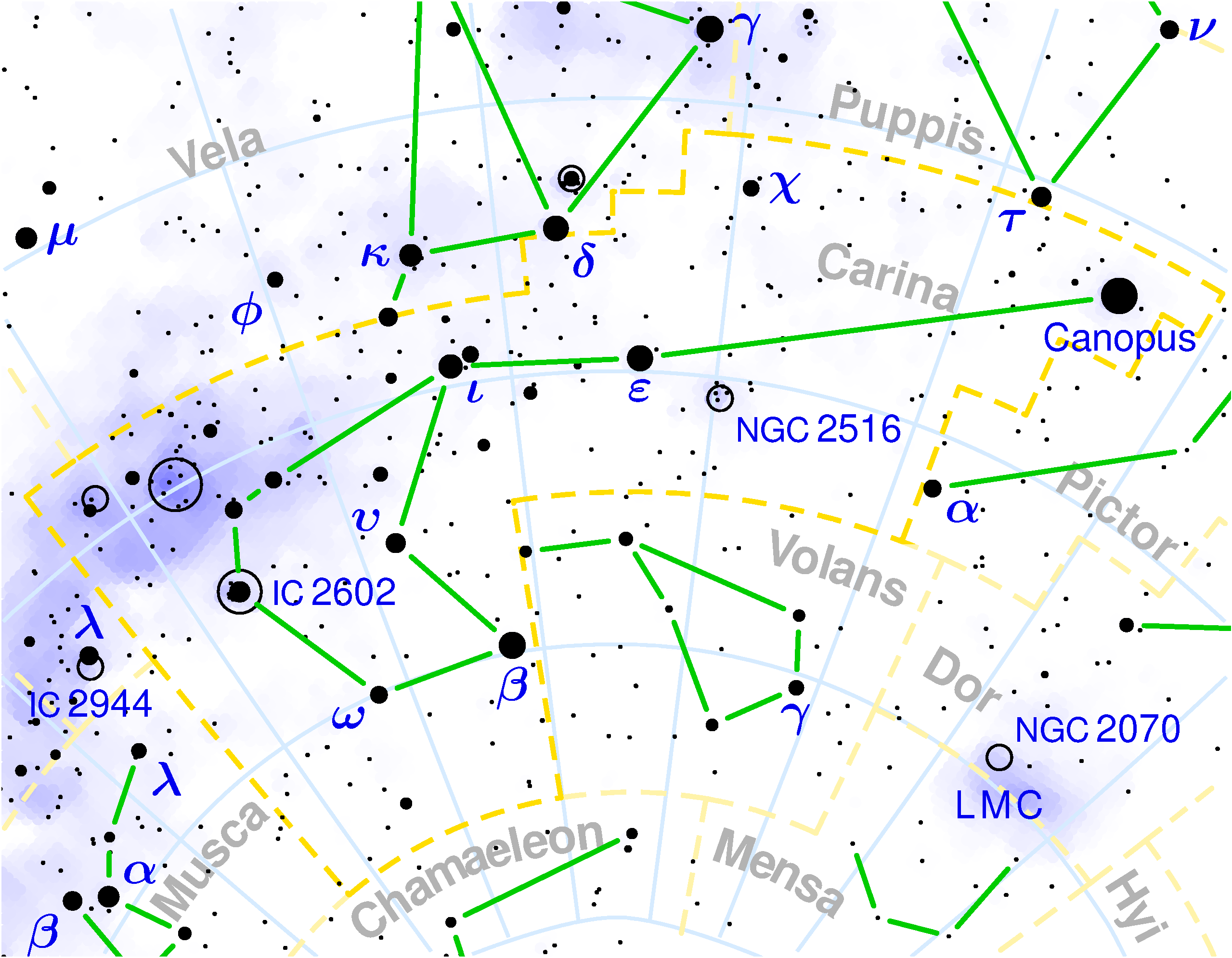
CARINA

Roberto Mura - Own work,
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
CC BY-SA 3.0, wikimedia
In antiquity there was a large constellation called the Argo Navis recalling the myth of the great ship of Jason and the Argonauts which was part of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy. The constellation was divided into three parts in the 18th Century: Carina, Puppis and Vela. The second brightest star in the skies, Canopus, and deep-sky objects are found in the Carina constellation making it one of the most fascinating constellations in the celestial sphere.
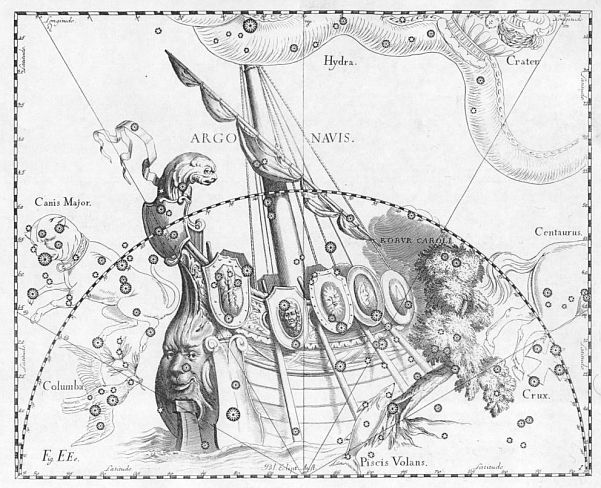
Johannes Hevelius - Atlas Coelestis.
Johannes Hevelius drew the constellation in Firmamentum Sobiescianum, sive Uranographia, his celestial catalogue in 1690,
Public domain, wikimedia
The stars in the Carina constellation are the most southern in the Argo Navis and cannot be seen from Italy. The first sightings of these stars were those of Eratosthenes, best known for his calculations of the Earth’s circumference, who was in Egypt when he saw the star Canopus. In 1843 the star Eta had a sudden increase in its brightness which made it brighter than Canopus, almost reaching the magnitude of Sirius.
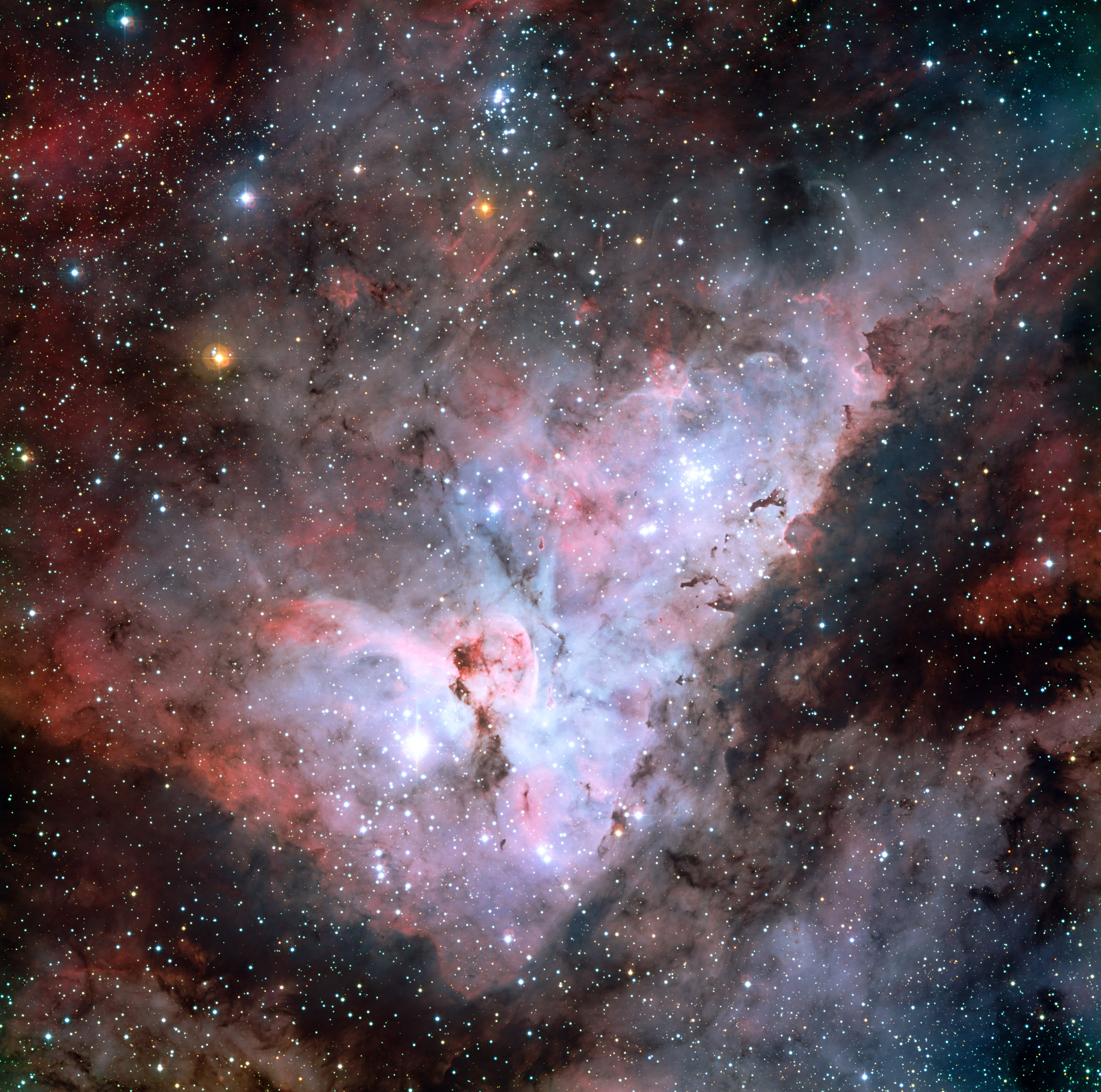
Eta Carinae is one of the most interesting variable stars in the skies. It has undergone numerous increases in its luminosity and it is thought that it is nearing explosion in its evolutionary stage to become a supernova or a hyper-nova or even a hazardous Gamma Ray Burst. Studies show that we are dealing with a hyper-giant star, one of the biggest we know of. It has a companion and is 5 million times brighter than the Sun.

ESO
CC BY 4.0, wikimedia
NGC 3372 is the Nebula of the Carina, the brightest emission nebula in the entire celestial vault, brighter even than the Nebula of Orion. It can be seen with a pair of binoculars. The Eta Carinae star is found inside the nebula. The diameter of the nebula spans 260 light-years and it is 7,500 light-years from us.

Roberto Mura Wikipedia in Italian - Trasferred from it.wikipedia su Commons da Jacopo Werther,
Public domain, wikimedia
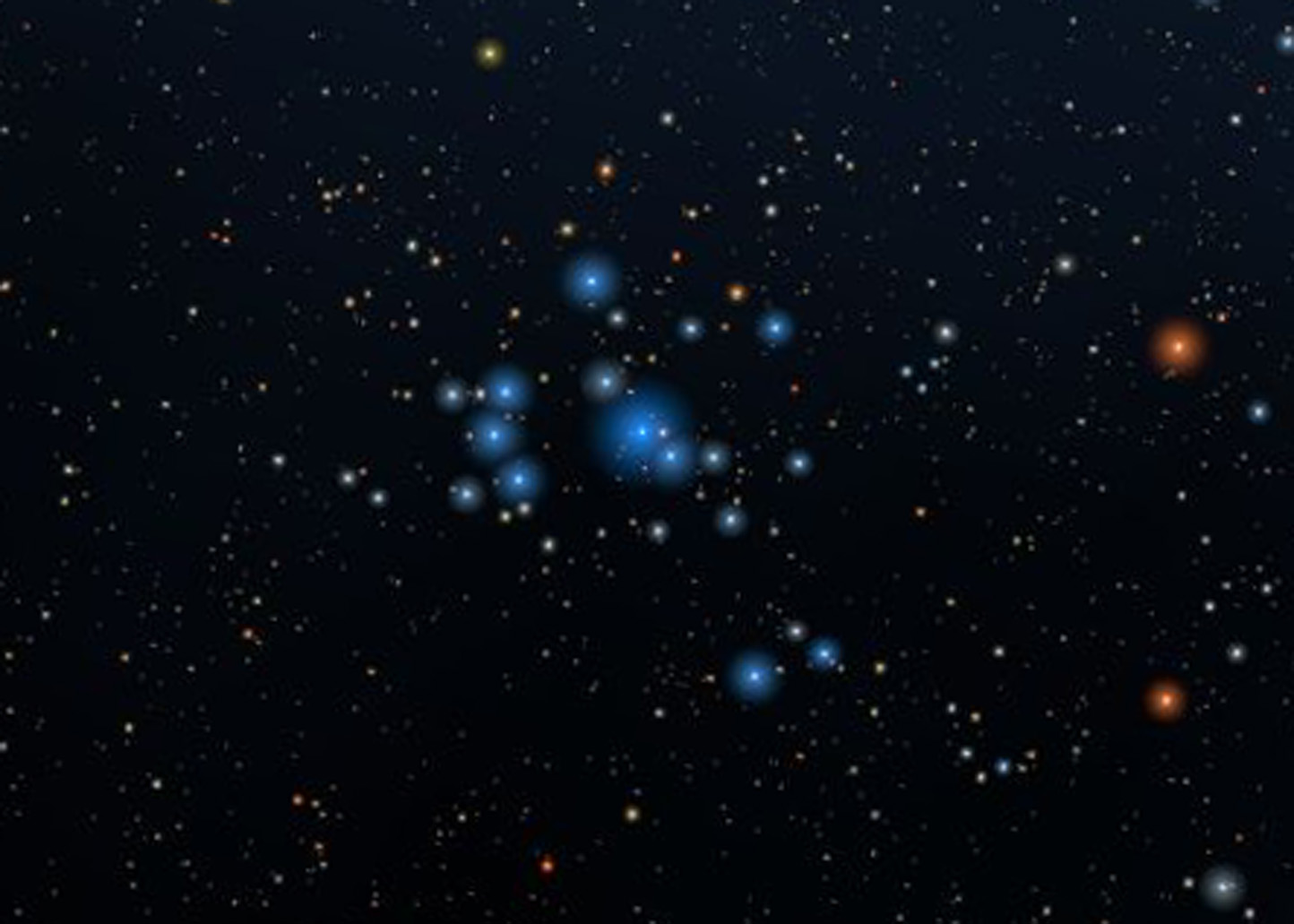
IC 2602 is an open cluster of stars called the ‘Southern Pleiades’. Similar to the open cluster of stars in Taurus of the same name, this one, too, is made up of young stars of less than 30 million years. It is about 500 light-years from Earth.
Southern Hemisphere: the constellation is visible almost all year. At the southern middle latitudes, from the end of April and the beginning of May, right after sunset, it can be seen high on the horizon towards the south.